Lateral Flow Assay
A lateral flow assay (LFA), also known as a lateral flow test or rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs), is a simple and rapid diagnostic tool used to detect the presence or absence of a specific substance or analyte in a sample.
Lateral flow assay offer several advantages, including rapid results (usually within minutes), simplicity of use (no complex equipment or specialized training required), and suitability for point-of-care testing. However, it's important to note that LFAs may have limitations in terms of sensitivity and specificity compared to more complex laboratory-based diagnostic tests. We at QAWaCh Bio have developed Quantitative LFA-based testing that uses a combination of a LFA test card and a smartphone application to give results within 10-15 minutes at the bed-side of the patient. Our quantitative LFA platform, called Q-Plat, is made ultra-sensitive by incorporating indigenously made detection molecules in our lab called Q-probe, that greatly enhances the sensitivity of all our assays.
What is Lateral Flow Assay ?
LFAs are commonly used in medical diagnostics, food safety testing, environmental monitoring, and various other fields. In the case of medical diagnostic tests utilizing lateral flow assay, a specific biomarker or protein undergoes biochemical interaction with its counter-molecule, such as antibodies, to aid in detection. The basic principle of a lateral flow assay entails the capillary action of fluids through a strip of nitrocellulose membrane, which incorporates specific components to facilitate the detection of the target analyte.
The test strip typically comprises major components such as the Sample Pad, Conjugate Pad, Nitrocellulose Membrane, Absorbent Pad, and a Backing Laminate on which all components of an LFA are assembled. Additionally, LFA-based tests can detect a single analyte or multiple analytes, allowing for the creation of multiplex LFAs. All the components of the LFA are encapsulated inside a cassette, complete with a result window and sample application area. Within the result window, there is usually a control line area and a test line area where the respective lines appear, facilitating easy interpretation of results
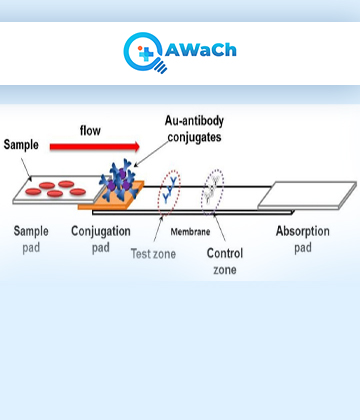
A Lateral Flow Assay (LFA), also known as a lateral flow test or rapid diagnostic test (RDT), serves as a straightforward and swift diagnostic tool used to determine the presence or absence of a specific substance or analyte in a sample. Furthermore, LFAs find applications in various fields, including medical diagnostics, food safety testing, and environmental monitoring. In medical diagnostic LFAs, a specific biomarker or protein undergoes biochemical interaction with its corresponding molecule, typically antibodies, for detection.
Strength:
The strength of Lateral Flow Assays lies in their speed and simplicity. LFAs provide rapid results, often within minutes, making them ideal for point-of-care testing. They are user-friendly and do not require complex equipment or specialized training. LFAs are versatile and can be designed to detect a single analyte or multiple analytes simultaneously, enabling multiplex testing.
Advantages:
Lateral Flow Assays offer several advantages, including their ability to deliver quick results at the patient's bedside or in the field. They are easy to use, making them accessible for a wide range of applications. LFAs are particularly suitable for scenarios where timely results are crucial, such as diagnosing infectious diseases or monitoring treatment effectiveness. They are cost-effective and require minimal sample preparation.
Recognitions:
LFAs are widely recognized for their role in simplifying diagnostic processes and expanding access to testing. They have revolutionized point-of-care testing, bringing diagnostics closer to patients. Lateral Flow Assays have been pivotal in medical diagnostics, particularly in resource-limited settings, where sophisticated laboratory facilities may be scarce.
Innovation:
Continuing the evolution of innovation in Lateral Flow Assays, QAWaCh Bio has introduced Quantitative LFA-based testing. This method incorporates a combination of a LFA test card and a smartphone application, delivering results within 10-15 minutes at the patient's bedside. Their platform, known as Q-Plat, enhances sensitivity by utilizing indigenously made detection molecules called Q-probe. This innovation significantly bolsters the sensitivity of LFAs, further amplifying their utility in healthcare and diagnostics.
